All you need to know about Thermal Energy Storage and decarbonizing the heat sector: we are pleased to release a new episode of The Basics & The Gaps.
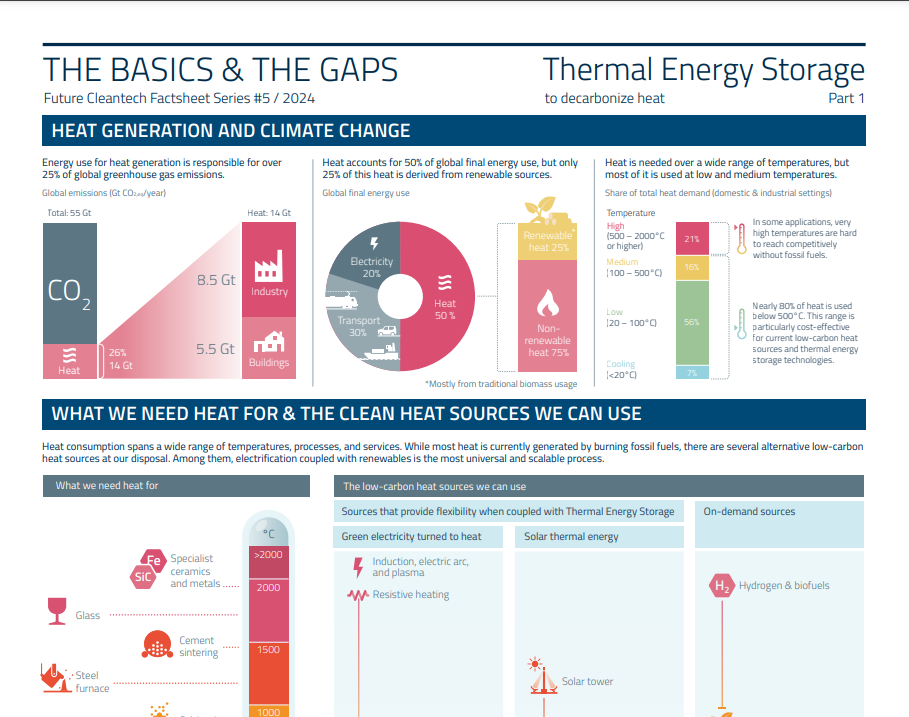
The heat sector plays a crucial role in the global economy and the energy transition: it accounts for 50% of global final energy use and over 25% of global greenhouse gas emissions. However, we are far away from decarbonizing this crucial sector, as only 25% of global heat production is currently derived from renewable sources. Thermal Energy Storage technologies can play a crucial role in decarbonizing the sector by:
✅ Capturing heat from several intermittent low-carbon energy sources, storing it at up to 1500ºC, and making it available on demand for both industrial and domestic applications.
✅ Facilitating renewable integration and electrification, increasing energy flexibility and security, and enabling consumption of lower-cost electricity.
✅ Improving energy efficiency by helping reuse waste heat from industrial processes.
While multiple Thermal Storage Technologies are commercially available, more support is needed to deploy them at scale and decarbonize the heat sector as fast as possible. Some key measures include:
✅ Expanding deployment of heat pumps, solar thermal energy, and geothermal energy in conjunction with district heating and thermal storage to decarbonize low and medium-temperature heat applications (below 500ºC), which constitute 80% of heat usage.
✅ Implementing targeted support schemes for low-carbon flexibility providers, establishing a suitable price on carbon, and avoiding extra taxes on electricity to help energy storage projects compete with existing polluting flexibility assets.
✅ Including energy efficiency, storage, and flexibility as integral elements of energy transition plans to support sustained, long-term investment in these sectors.
To learn more and to see the Factsheet in German, French, or Spanish, click here.